Visits: 837
ISO 21378 Audit data collection data model definition based on UN/CEFACT CCTS and comparison with other standards including XBRL GL
We are currently investigating other standards to clarify the data architecture of the audit data collection. The goal is to define an ADS data model based on the Core Component Technical Specification (CCTS) defined in ISO 15000-5.
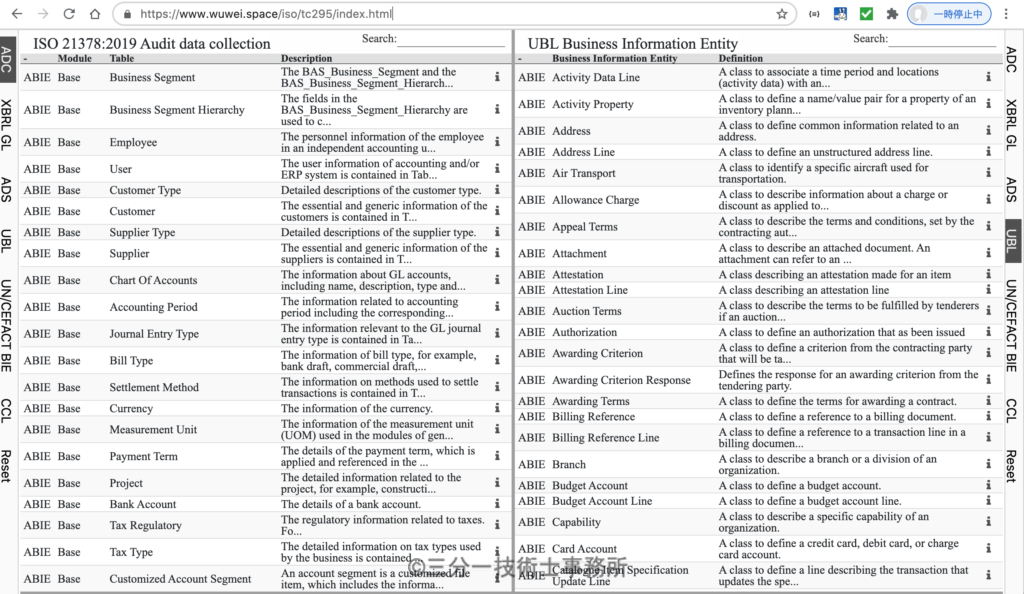
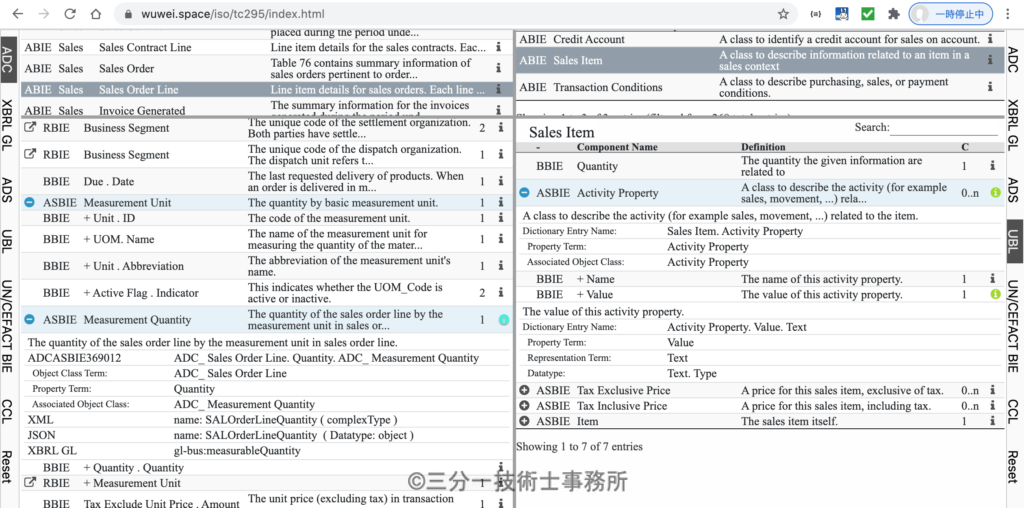
A comparison site (https://www.wuwei.space/iso/tc295/index.html) is in development. This site helps to check similarities and differences between following data model, namely, UN/CEFACT core component libraries and business information entities, OASIS Universal Business Language (UBL), AICPA’s audit data standards (ADS) including XBRL GL, ISO 21378 audit data collection. This site is constructed by analyzing the data structure of each standard data. Common building blocks are core components (CCL, BCC, ASCC, ACC) and business information entities (BBIE, ASBIE, ABIE).
Detailed mapping information provides the basic data for the project and helps the project progress.
I introduced RBIE as an extension. Although these fields are defined in CCS as Basic Business Information Entity (BBIE), the Relationship Business Information Entity (RBIE) is required to define ISO 21378, which explicitly defines the primary and foreign key relationships between tables. Many fields in the table state that this field must match the unique identifier field in the XXX table.
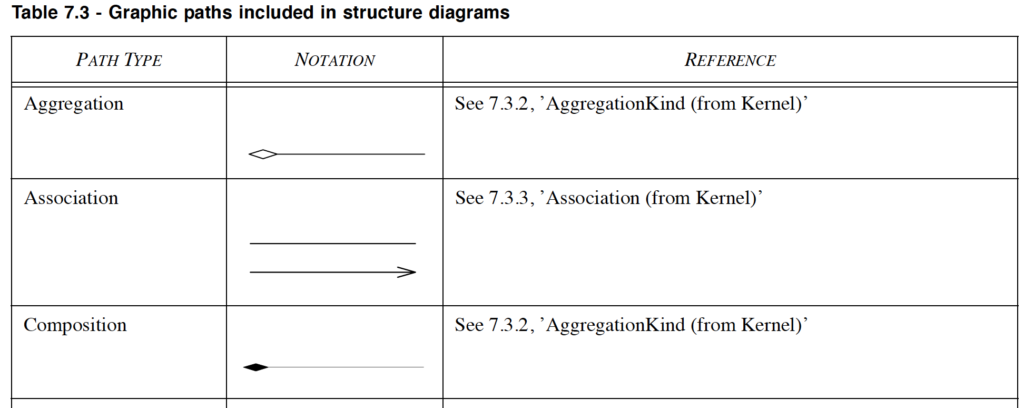
Following is Graphical paths diagram from UML Superstructure Specification, v2.4.1
The graphic paths that can be included in structure diagrams are shown in Table 7.3.
 Aggregate Business Entity (ABIE) uses Association Business Entity (ASBIE) as aggregation not association. A relationship from a reference identifier to it’s associated unique identifier in referenced class can be defined by association.
Aggregate Business Entity (ABIE) uses Association Business Entity (ASBIE) as aggregation not association. A relationship from a reference identifier to it’s associated unique identifier in referenced class can be defined by association.
UN/CEFACT Core Components Technical Specification (CCTS)
Core Components Technical Specification – Part 8 of the ebXML Framework 15 November 2003 Version 2.01 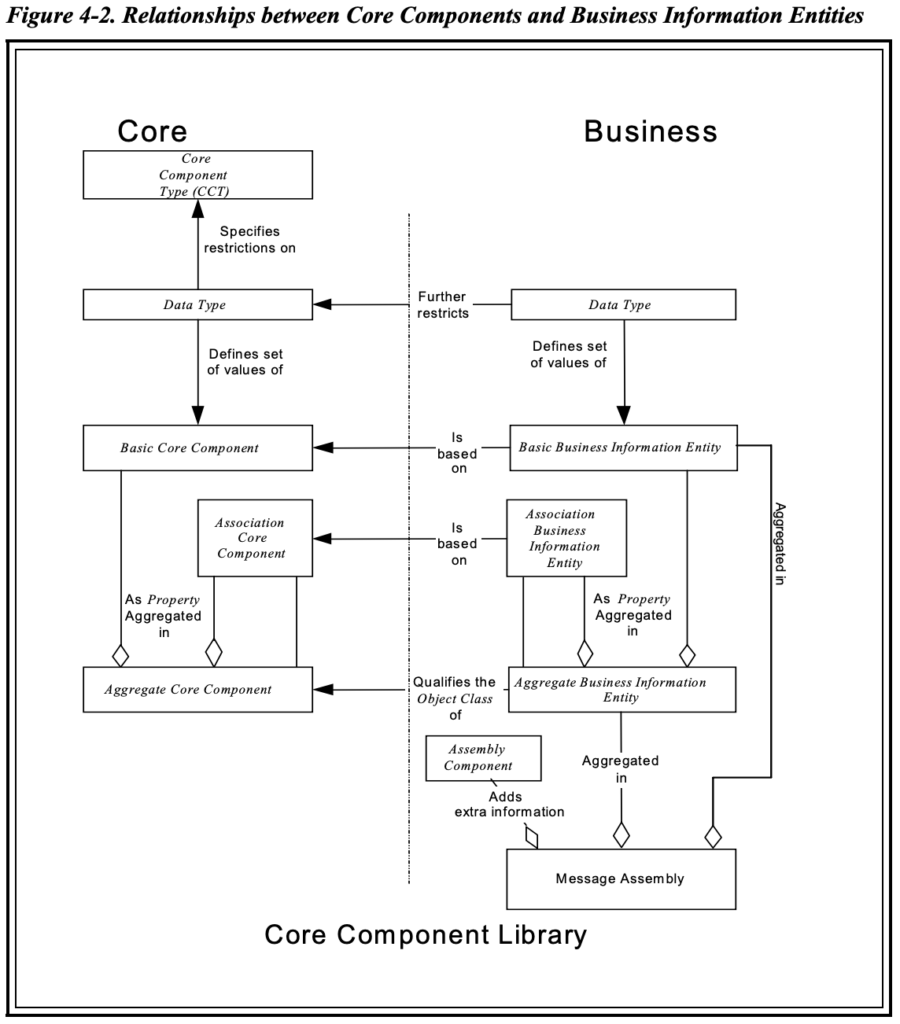
Association Business Information Entity defines Aggregation in CCTS. Association is required to define Audit data collection data model.
[Definition]
Business Information Entity (BIE)
A piece of business data or a group of pieces of business data with a unique Business
Semantic definition. A Business Information Entity can be a Basic Business Information
Entity (BBIE), an Association Business Information Entity (ASBIE), or an Aggregate
Business Information Entity (ABIE).[Definition]
Basic Business Information Entity (BBIE)
A Business Information Entity that represents a singular business characteristic of a
specific Object Class in a specific Business Context. It has a unique Business Semantic
definition. A Basic Business Information Entity represents a Basic Business Information
Entity Property and is therefore linked to a Data Type, which describes it values. A Basic
Business Information Entity is derived from a Basic Core Component.[Definition]
Association Business Information Entity (ASBIE)
A Business Information Entity that represents a complex business characteristic of a
specific Object Class in a specific Business Context. It has a unique Business Semantic
definition. An Association Business Information Entity represents an Association
Business Information Entity Property and is associated to an Aggregate Business
Information Entity, which describes its structure. An Association Business Information
Entity is derived from an Association Core Component.[Definition]
Aggregate Business Information Entity (ABIE)
A collection of related pieces of business information that together convey a distinct
business meaning in a specific Business Context. Expressed in modelling terms, it is the
representation of an Object Class, in a specific Business Context.[Note]
The term Core Component is used as a generic term that encompasses Basic Core
Components, Association Core Components, Aggregate Core Components, and their
associated Core Component Types. Equally, the term Business Information Entity is used
as a generic term encompassing Basic Business Information Entities, Association
Business Information Entities, and Aggregate Business Information Entities.
Comparison based on CCTS
Comparison Service
Using the same data types and modeling based on the UN/CEFACT core component library and Core Component Technical Specification (CCTS) makes it easy to identify similarities and differences between standards.
This site provides detailed information on data model definition for ISO 21378 Audit data collection and UBL Business information entity.
This site uses the ISO 21378 data model defined using an Excel workbook similar to CCL 20A by UN/CEFACT.
You can find how to use on this page.
ISO 21378 Audit data collection
ADCS
This frame contents are based on ADC.xlsx
ISO 21378 Audit data collection
This document establishes common definitions of accounting data elements and provides the information necessary to extract relevant audit data.
NOTE For the purpose of this document, “audit” refers to an examination of an entity’s financial and financial related records in order to check that they are fairly presented.
This document is applicable to the bridging of understanding among auditors, auditees, software developers and IT professionals, and creating a mechanism for expressing the information, common to accounting, in a manner independent of accounting and ERP systems. This document serves as a foundation for local data extraction efforts in the areas of general ledger, accounts receivable, sales, accounts payable, purchase, inventory, and property, plant and equipment.
Data files
ISO 21378 was developed independently of UN/CEFACT CCTS as a CSV file format.
This research project defines ISO 21378 Audit data collection data model based on CCTS.
Generate a Excel file and convert to following JSON file.
Aggregate Business Information Entity
Basic Business Information Entity / Association Business Information Entity
Data Type
UN/CEFACT
Core Components Library (CCL) 20A
Data files
CCL 20A (Excel)
This Excel contains sheets for Business Information Entity and Core Component Library. Each sheet is exported as a tab separated file and converted to following JSON files.
Business Entity Information
Aggregate Business Information Entity
Basic Business Information Entity/Association Business Information Entity
qualified Data Type
unqualified Data Type
Core Component
Aggregate Core Component
Basic Core Component / Associate Core Component
unqualified Data Type
UBL
OASIS UBL 2.3
UBL is an international standard ISO/IEC 19845:2015 Information technology — Universal business language version 2.1 (UBL v2.1)
The electronic version of this International Standard can be downloaded from the ISO/IEC Information Technology Task Force (ITTF) web site.
Most current version by OASIS is UBL 2.3 (https://docs.oasis-open.org/ubl/csprd01-UBL-2.3/UBL-2.3.html)
ISO is identical to the document under OASIS.
Data files
Following link provides data model as an Excel book.
Document models of information bundles:
https://docs.oasis-open.org/ubl/csprd02-UBL-2.3/mod/
A file named EBL-Entities-2.3.xls contains many sheets. Export each sheet as TSV file and convert them to JSON files.
Aggregate Business Information Entity
Basic Core Component / Associate Core Component
Data Type
AICPA
Audit Data Standards
The Assurance Services Executive Committee’s Emerging Assurance Technologies Task Force established the Audit Data Standard working group to develop a standardized data model that facilitates the use of enhanced analytics.
https://www.aicpa.org/interestareas/frc/assuranceadvisoryservices/auditdatastandards.html
Audit Data Standards – Overview
One of the challenges that management and auditors face is obtaining accurate data in a usable format following a repeatable process. As a result, this working group has developed voluntary, uniform audit data standards that identify the key information needed for audits and provide a common framework covering: (1) data file definitions and technical specifications, (2) data field definitions and technical specifications, and (3) supplemental questions and data validation routines to help auditors better understand the data and assess its completeness and integrity. The standards are offered in either of the following two file formats: (1) flat file format (pipe-delimited UTF-8 text file format) and (2) Extensible Business Reporting Language Global Ledger Taxonomy Framework (XBRL GL).
- Base Standard as of July 2015
- General Ledger Standard as of July 2015
- Order to Cash Standard as of July 2015
– Order to Cash Subledger Standard as of July 2015 includes information specific to Order to Cash accounts. - Procure to Pay Standard as of July 2015
– Procure to Pay Subledger Standard includes information specific to Procure to Pay accounts. - Inventory Standard as of March 2017
– Inventory Subledger Standard includes information specific to Inventory accounts. - Fixed Asset Standard as of December 2017
– Fixed Asset Subledger Standard includes field and file information specific to fixed asset accounts.
Data files
Audit Data Standards was developed independently of UN/CEFACT CCTS.
This research project defines ADS data model based on CCTS.
Export each pdf file as an Excel book and convert to following JSON file.
Aggregate Business Information Entity
Basic Business Information Entity / Association Business Information Entity
Data Type
XBRL Global Ledger: Transactional Reporting
XBRL GL Framework
This taxonomy (a modular set) provides a standardized format for representing the data fields found in accounting and operation systems. The modular set consists of the following modules: COR (Core), BUS (advanced business concepts), MUC (concepts that represent multicurrency information), USK (concepts specific to the US, UK, and other Saxonic jurisdictions), TAF (concepts related to the tax audit file), SRCD (concepts that represent explicit mappings to XBRL taxonomies for financial reporting) and EHM (concepts related to inventory and fixed assets).
COR is the foundational module. It includes core data fields that are the base for the representation of all types of information with XBRL GL.
BUS augments COR with data fields found in accounting and operation systems that will allow organizations to track much more detail as part of every entry. This taxonomy represents inventory and business metrics, organizational detail and the Entity Information section, and other common items to supplement the resources, agents and events that represent the customer, vendor and employee related transactional detail.
MUC adds data fields found in accounting and operation systems that will allow organizations to track much more detail as part of every entry. This includes detail for the Entity Information section, additional sections necessary for other add-on modules, and information for business metrics/inventory tracking.
USK provides data fields found in accounting and operation systems that will allow organizations to tag journal entries, accounting master files, and historical status reports with additional information necessary for more sophisticated accounting needs common to Saxonic (US, UK, Australia, Canada, and other jurisdictions) in XBRL.
TAF adds data fields needed for tax and tax audit. The addition of these fields enables XBRL GL to be used by the international tax agencies and was developed with the input of groups such as the OECD SAF-T group and the OASIS Tax XML group.
SRCD provides data fields that facilitate the link between detailed data represented with XBRL GL and end reporting represented with XBRL taxonomies for financial reporting (XBRL) or other XML schemas.
EHM (Enhanced Measurable) module provides fields specific to the representation of inventory and fixed assets.
Each module can be seen as an extension to the Core module, but it is more worthwhile to look at the modules as parts of a whole, even though it is not essential to use all of them.
https://www.xbrl.org/int/gl/2016-12-01/gl-framework-2017-PWD-2016-12-01.html
Data files
XBRL GL was developed independently of UN/CEFACT CCTS.
This research project defines XBRL GL data model based on CCTS.
Generate a Excel file from XBRL taxonomy and convert to following JSON file.
Aggregate Business Information Entity
Basic Business Information Entity / Association Business Information Entity
Data Type